背景
什么是点云
点云是空间中一系列的点,每个点有空间中的 X、Y、Z 坐标。通过一系列的点构成的点云,描绘出地形的一种数据。在使用无人机做地形测量中,由无人机拍摄的照片经过摄影测量计算,最终输出的一种典型格式就是点云格式。

为什么要根据地形抽稀
在通过摄影测量输出的点云中,数量级是通常的地形处理软件(如 CAD)无法处理的,以国内用的比较多的 CASS 为例,处理由几万点组成的地形数据,已经达到极限。因为之前这些软件适配的都是通过人工在地形上进行采集数据点,人工一般间隔 3-5 米采集一个点。而无人机输出的点云间隔可以在 5cm 甚至更低。
在常规的处理流程中,一般先将无人机输出的点云,经过专业软件识别地形与非地形(剔除建筑,车辆,植被点云),保留地形点,再将地形点按距离平均抽稀成 0.5 米一个点左右。而此时点数可能依然在几十万级别。接下去的抽稀就要考虑地形因素,一般来说需要保证 3-5 米一个点。同时,在地形平缓的部分,可以适当稀疏,在地形起伏部分,需要适当加密。以保证在足够少的点数下,同样可以描绘出地形。确保后续处理算量的准确度。
核心思想
- 读取点云
- alphashape 算法,取范围点
- 创建三角网
- 去除三角网中内角有大于 120 度的三角形
- 将整幅图划分 3*3 米网格(用于确保每个网格中都存在点,防止在平整地区全部判断为非关键点,被去除)
- 遍历每个点
- 如果点判断为范围点,直接保留,对该点所处的网格标记,继续遍历
- 如果点判断为非范围点,找到以该点为顶点的所有三角形
- 计算空间三角形的面的法向量
- 判断每个空间三角形所在的面的法向量夹角
- 如果存在某个法向量夹角大于一个阈值,即判定该点为关键点,保留,对该点所处的网格标记,继续遍历
- 判断即非范围点,也非关键点,则去除
- 检查是否每个网格都有至少一个点,如没有,找点放入
代码实现
读取点云
这边读取的是 dat 格式的点云文件
def readDAT(path):
point_list = []
with open(path) as f:
line = f.readline()
while line:
str_list = line.rstrip().split(',')
point = [float(str_list[2]), float(str_list[3]), float(str_list[4])]
point_list.append(point)
line = f.readline()
return point_list
alphashape 算法,取范围点
具体可参考 https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape ,这里只做了调用
PS:其实在这个抽稀算法中,alphashape 不重要,因为后续每 3*3m 网格会包含一个点,是否取到点的范围线问题不大
def find_shape(self, alpha=0.15):
points_2d = [(self.points[i][0], self.points[i][1]) for i in range(len(self.points))]
# alpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points)
alpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_2d, alpha=alpha)
if type(alpha_shape) == Polygon:
x, y = alpha_shape.exterior.coords.xy
self.shape_points = [[x[i], y[i]] for i in range(len(x))]
return True, '查找范围成功'
else:
print('查找范围失败,减小 alpha 值')
return False, '查找范围失败,减小 alpha 值'
创建三角网
参考:https://github.com/HakanSeven12/Delaunator-Python, 这里只做调用
def create_coordinates(self):
triangles = Delaunator(self.points).triangles
# halfedges = Delaunator(self.points).halfedges
# hull = Delaunator(self.points).hull
# coords = Delaunator(self.points).coords
coordinates = []
for i in range(0, len(triangles), 3):
coordinates.append([
self.points[triangles[i]],
self.points[triangles[i + 1]],
self.points[triangles[i + 2]]])
self.coordinates = coordinates
去除三角网中内角有大于 120 度的三角形
遍历三角形,根据每个三角形的平面坐标计算三个内角
def clean_above_120_coordinate(self):
new_coordinates = []
for coordinate in self.coordinates:
a = math.sqrt((coordinate[0][0] - coordinate[1][0]) * (coordinate[0][0] - coordinate[1][0]) +
(coordinate[0][1] - coordinate[1][1]) * (coordinate[0][1] - coordinate[1][1]))
b = math.sqrt((coordinate[1][0] - coordinate[2][0]) * (coordinate[1][0] - coordinate[2][0]) +
(coordinate[1][1] - coordinate[2][1]) * (coordinate[1][1] - coordinate[2][1]))
c = math.sqrt((coordinate[2][0] - coordinate[0][0]) * (coordinate[2][0] - coordinate[0][0]) +
(coordinate[2][1] - coordinate[0][1]) * (coordinate[2][1] - coordinate[0][1]))
A = math.degrees(math.acos(clamp((a * a - b * b - c * c) / (-2 * b * c), -1, 1))) # 夹角1
B = math.degrees(math.acos(clamp((b * b - a * a - c * c) / (-2 * a * c), -1, 1))) # 夹角2
C = math.degrees(math.acos(clamp((c * c - a * a - b * b) / (-2 * a * b), -1, 1))) # 夹角3
# print(A, B, C)
if A >= 120 or B >= 120 or C >= 120:
continue
new_coordinates.append(coordinate)
self.coordinates_without120 = new_coordinates
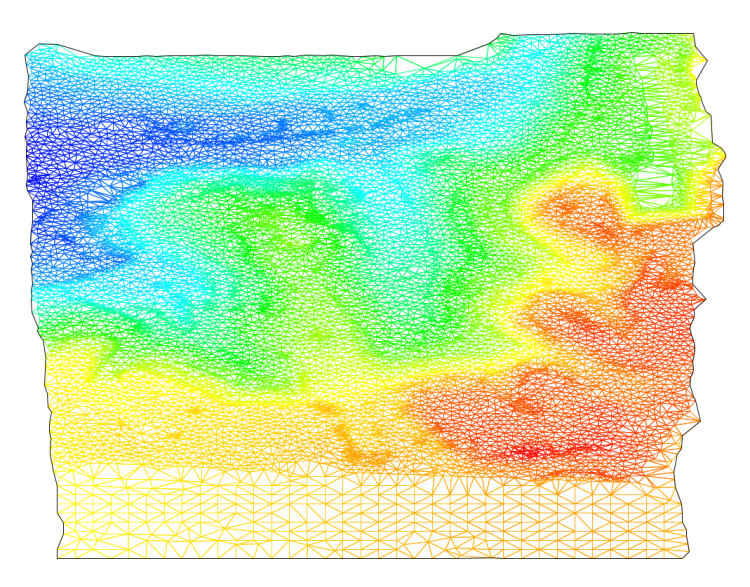
去除 120 度三角网后的地形三角网,黑线为 AlphaShape 取出的范围
将整幅图划分 3*3 米网格
(用于确保每个网格中都存在点,防止在平整地区全部判断为非关键点,被去除)
def init_grid(self, distance=3.5):
# self.x_y_min_max 是平面上最上下左右的范围
distance_x = self.x_y_min_max[1] - self.x_y_min_max[0]
distance_y = self.x_y_min_max[3] - self.x_y_min_max[2]
num_x = distance_x // distance
num_y = distance_y // distance
num_x += 1
num_y += 1
grid = [[False for i in range(int(num_x))] for j in range(int(num_y))]
return grid
核心流程(遍历、判断、抽稀)
def thinning_task(self, limit_angle, limit_distance, points):
self.grid = self.init_grid(distance=limit_distance)
new_points = []
for point in points:
# 判断是否为边界点
if is_point_in_shape(point, self.shape_points):
new_points.append(point)
self.set_grid(point, limit_distance)
continue
# 找到以该点为顶点的三角形
coordinates_with_point = search_coordinates_with_point(self.coordinates_without120, point)
if len(coordinates_with_point) == 0:
continue
# 判断是否为特征点
if is_characteristic_point(coordinates_with_point, limit_angle):
new_points.append(point)
self.set_grid(point, limit_distance)
# 补齐网格点
for point in points:
# 判断这个点所处的格子里是否有点了
if self.is_grid_false(point, limit_distance) is False:
new_points.append(point)
self.set_grid(point, limit_distance)
return new_points
- 如果点判断为范围点,直接保留,对该点所处的网格标记,继续遍历
def is_point_in_shape(point, shape_points):
if shape_points is None:
return False
for shape_point in shape_points:
if point[0] == shape_point[0] and point[1] == shape_point[1]:
return True
return False
- 如果点判断为非范围点,找到以该点为顶点的所有三角形
原来的代码
def search_coordinates_with_point(coordinates, point):
# 找到以该点为顶点的三角形
coordinates_with_point = []
for coordinate in coordinates:
for coordinate_point in coordinate:
if coordinate_point[0] == point[0] and coordinate_point[1] == point[1]:
coordinates_with_point.append(coordinate)
return coordinates_with_point
因为效率低下,后来使用 Python 内置数据库 SQLite 用于存点和找点,速度大幅提升
def search_coordinates_with_point(self, point):
# 找到以该点为顶点的三角形
coordinates_with_point = []
cur = self.con.cursor()
for i in range(1, 4):
cur.execute('select * from test where x%s=? and y%s=?' % (i, i), (point[0], point[1]))
results = cur.fetchall()
for r in results:
# print(r)
coordinate = [[r[0], r[1], r[2]], [r[3], r[4], r[5]], [r[6], r[7], r[8]]]
coordinates_with_point.append(coordinate)
return coordinates_with_point
- 判断是否为特征点
(计算该点为顶点的三角形的面的法向量,判断法向量之间的夹角)
def is_characteristic_point(coordinates_with_point, limit_angle):
range_angle1 = limit_angle
range_angle2 = 180 - limit_angle
vectors = []
for coordinate in coordinates_with_point:
# 计算每个三角形的空间法向量
flag, dx, dy, dz = nv.CalNormalVector(coordinate[0][0], coordinate[0][1], coordinate[0][2],
coordinate[1][0], coordinate[1][1], coordinate[1][2],
coordinate[2][0], coordinate[2][1], coordinate[2][2])
if flag:
vectors.append((dx, dy, dz))
for i in range(len(vectors)):
# 只要有一个任意两个空间法向量直接的夹角大于 limit_angle,即判断这个点为特征点,保留
# break_flag = False
for j in range(len(vectors)):
if i == j:
continue
angle = nv.CalAngle(vectors[i], vectors[j])
# print(angle)
if range_angle1 < angle < range_angle2:
return True
return False
- 检查是否每个网格都有至少一个点,如没有,找点放入
def set_grid(self, point, distance):
index_x = int((point[0] - self.x_y_min_max[0]) // distance)
index_y = int((point[1] - self.x_y_min_max[2]) // distance)
self.grid[index_y][index_x] = True
pass
def is_grid_false(self, point, distance):
index_x = int((point[0] - self.x_y_min_max[0]) // distance)
index_y = int((point[1] - self.x_y_min_max[2]) // distance)
return self.grid[index_y][index_x]
数据验证
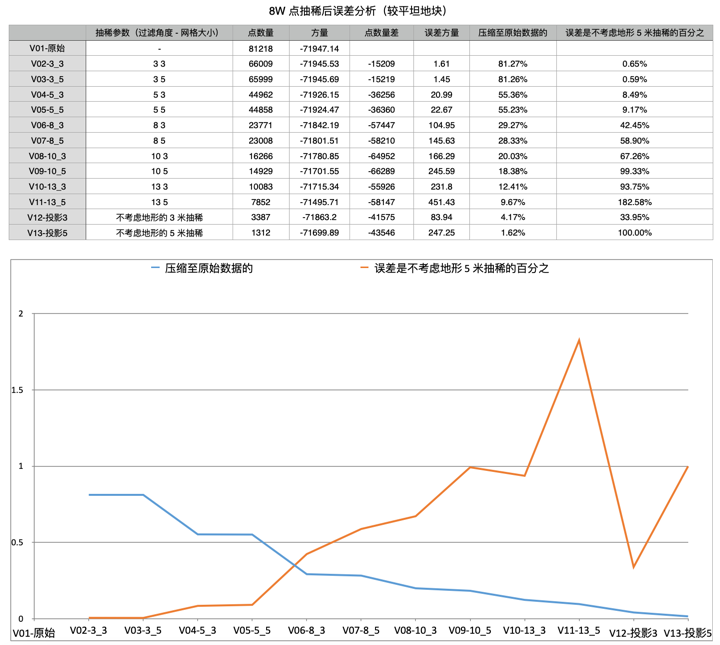
8wpoint.dat (limit_angle=8, limit_distance=3) 测试数据
抽稀前
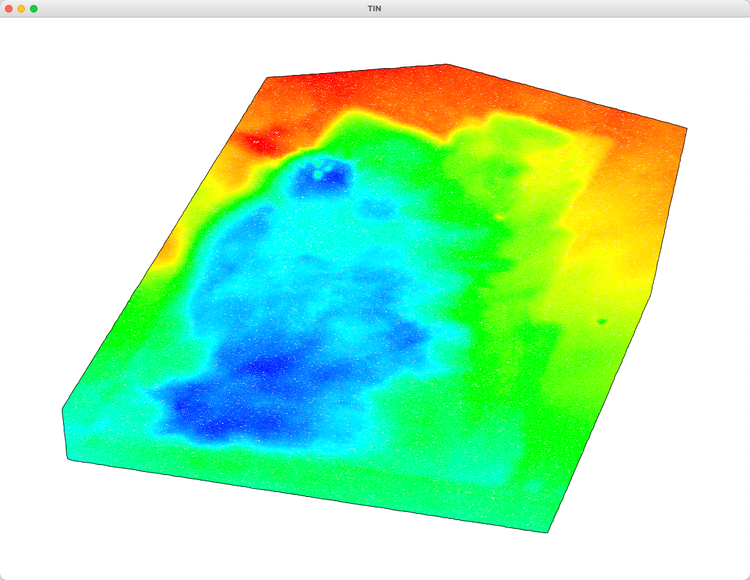
抽稀后
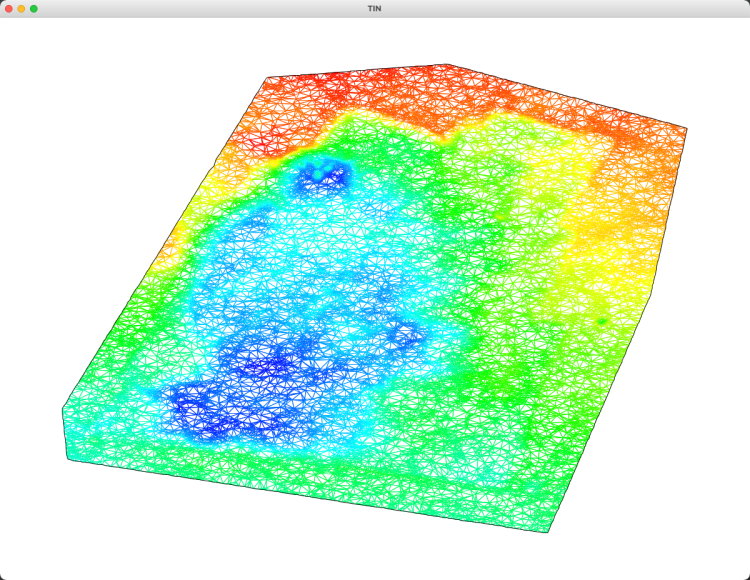
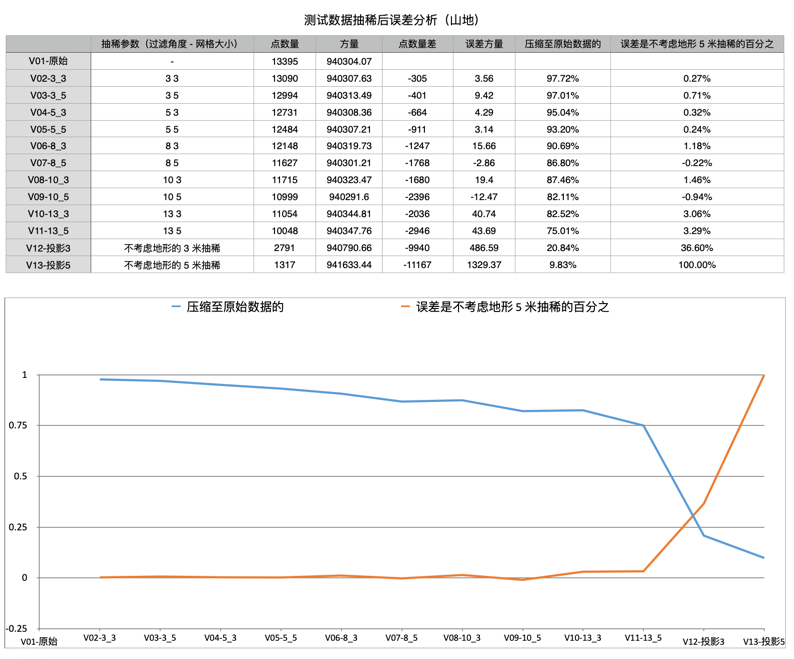
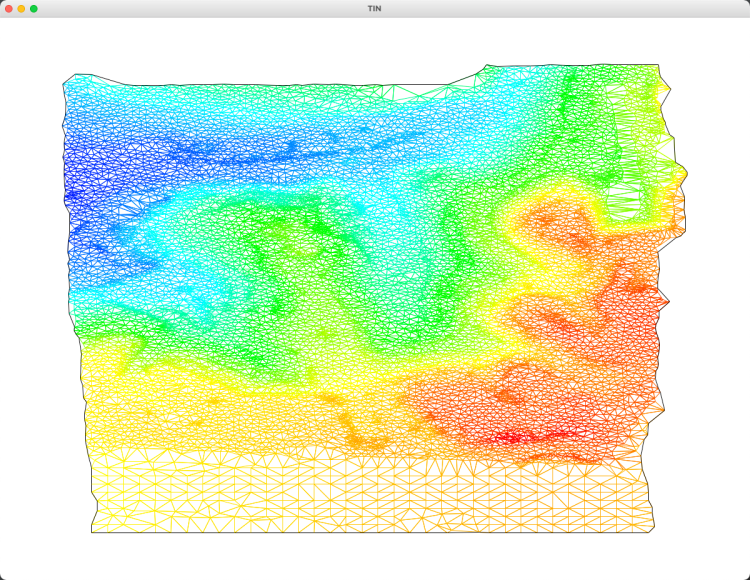
test.dat (limit_angle=10, limit_distance=5) 测试数据
抽稀前
抽稀后
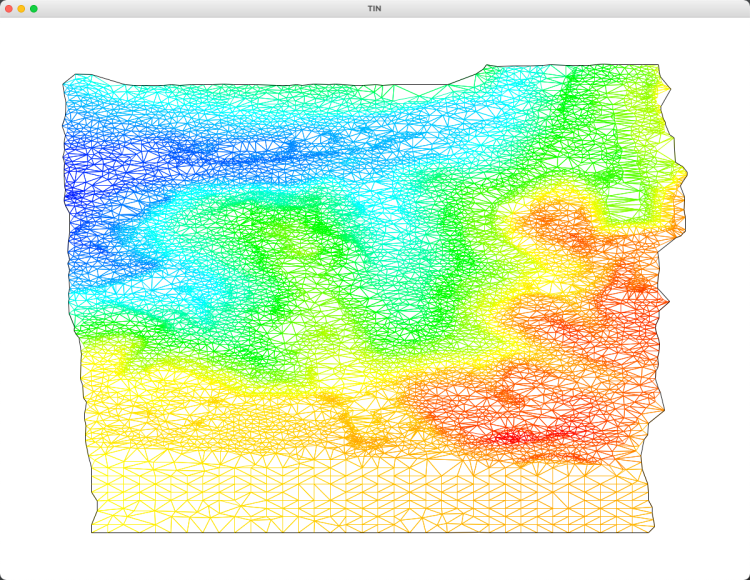
误差分析